Since the economic reforms of 1991, India has emerged as an important nation in world economic order. Currently India is 3rd largest economy in PPP terms with GDP size of USD 10.4 Trillion and 6th largest economy in nominal terms with GDP size of USD 2.69 trillion. It has foreign exchange reserves in the tune of USD 400 billion. The current GDP growth rate estimate for India is more than 7 %. Though these numbers are indicative of India’s importance in world economy, yet it has a current account deficit which expected at 2.8 % of GDP, this primarily due to oil imports as India imports over 82 per cent of its crude requirement through imports. The Current Account Deficit (CAD) exerts pressure on Indian Currency INR as it depreciates against USD. The current account deficit is funded through capital flows and one of the important sources of Capital Flows is NRI Remittances. According to the World Bank report India Tops the global remittance amounting to USD 80 billion. The bulk of the Remittance are originates from GCC Countries. In light of such parameters and conditions, this paper explores the Economic linkages of GCC and India and how it will help India for its quest for Economic Powerhouse in the future.
Key Words: Current Account Deficit, NRI Remittances, Oil
1. INTRODUCTION
Since the economic reforms of 1991, India has emerged as one of the Important economy in the world with a GDP size of USD 2.60 Trillion and in Purchasing power parity terms around USD 10.40 Trillion. The Indian GDP growth rate is 7.30 % which is one of the fastest in current times. The Foreign exchange reserves are around USD 400 billion. In spite of these remarkable numbers India has a current account deficit which expected at 2.8 % of GDP, this primarily due to oil imports, as India meets over 82 per cent of its crude requirement by way of imports. The Current Account Deficit (CAD) exerts pressure on Indian Currency INR which depreciated against USD at all time low of INR 74.55 / USD on October 9th , 2018. Same time the International Crude Oil price was hovering around more than USD 80 per barrel. This relationship International Crude Oil and USD / INR pair is very dynamic because India Imports more than 80 % of its oil requirement. In 2017 India has imported Crude oil worth USD 60.20 billion which was 6.90% of the world oil imports.1
India‟s imports from Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) are 42% of its overall oil imports.The major importers of oil to India are Saudi Arabia, UAE and Qatar. The GCC is India‟s largest regional-bloc trading partner, which accounted for USD 104 billion. The largest expatriate community in GCC is made of Indians with estimate of 10 million are working and living in the GCC region. According to World Bank, India will receive remittances around USD 80 billion this year, followed by China (USD67 billion), Mexico and the Philippines (USD 34 billion each), and Egypt (USD 26 billion). The majority of the remittances received by India are originated from GCC area. This research paper highlights India‟s strong linkages with the GCC and explores the further economic tie-up with GCC considering today‟s dynamic socio-political scenario with keeping in mind that India‟s quest for becoming economic powerhouse in future.
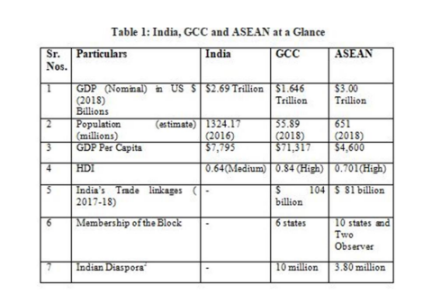
Table 1 clearly explains the importance of GCC block in comparison with ASEAN. The three important factors that give cutting edge to India‟s relationship with GCC as against ASEAN are
. Oil
. Remittances
. Indian Diaspora in GCC
Looking at the facts presented, it is up most vital that India need to nurture its tie-up with GCC in forthcoming years.
1. ANALYSIS OF INDIA-GCC LINKAGES<
As a result of globalization the inter linkages of Indian Economy with trade blocks and financial markets has been significantly increased. Such linkage and interdependence of different regions attracts the attention of policy makers, investors, fund managers and academicians in order to estimate what could be the future of inter-regional equations. This concept paper based upon the secondary data explores the India‟s would be cooperation with GCC Countries. Such collaboration is significant as India is aiming at a tag of USD 5 Trillion economy in forthcoming years.
There are few studies done earlier about the linkage across India and GCC. It is observed that the GCC investments in India,China and Africa are occurring on an unprecedented scale. These Investments are more comfortable due to diasporic links and cultural ties. (Abdelal et.al 2008).It is not only India has substantial interest in GCC but China also interested in the GCC region due to its oil richness.(Habibi, 2011). China also shown significant interest in recent years in GCC, according to Xuming QIAN & Jonathan FULTON (2017), the China-GCC economic relations can be expected to intensify due to FTA. The FTA will also enhance cooperation opportunities for China and the GCC under the “Belt and Road” Initiative, which will play an important role in expanding China‟s regional presence. It is also observed that GCC states are altering companies‟ strategies rather than Wall Street. The India –GCC bilateral export is positively determined by the size of economies, trade openness Common Colony and Diaspora and it is negatively determined by distance between India-GCC and import tariffs. (Alam & Ahmed, 2018). Regarding the increase of import of crude oil by India and steep increase of crude oil price in global market can cause damage to Indian Economy and India‟s lack of having a credible fuel policy is a matter of high concern (Venkataraman, 2018).
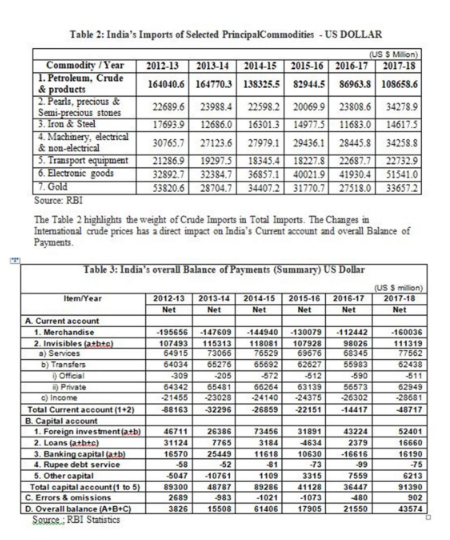
The perennial deficit of current account is more to do with the merchandise that too in particular oil imports, which in turn dependent on the global crude prices. The Demand Supply, Geopolitical situation affects the International Crude Prices. India is more vulnerable to this price fluctuation as approximately 64.0 % of her oil need is imported from sensitive and volatile Middle East region. The International Energy Agency predicts China will import 70 percent of its oil from the GCC by 2015 (Teslik,2008)4 . The China is also a important player to watch regarding the import of crude oil from GCC. The volatility of oil price affects GCC as well as India. Whenever the oil price goes up,India‟s import bill soars, but if oil price goes down it effects the economy and investment scenario of GCC, which results into less exports from India to GCC and shortfall in remittance to India from the GCC region. Thus India is vulnerable to the oil price volatility. In light of such situation India needs her safety net so that it could manage the impact of Oil price volatility in a better way. The INR priced oil imports and special lines of credit to GCC countries in terms of bilateral trade with India may help in better management of international trade and finance. India with its great experience in Central Banking System .India‟s Central Bank, RBI was established in 1935, it can guide the GCC countries to formulate their own monetary union so to trade with India and rest of the world. The Merger and Acquisition is on rise in GCC , Indians can help in terms of its vast management talent pool to restructure the existing businesses in GCC area as it fully understand the cultural issues of that region.
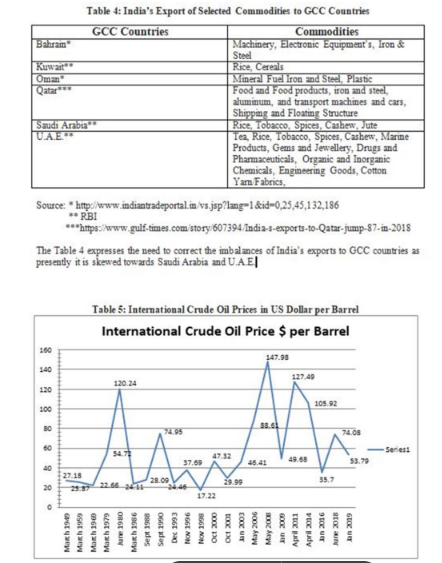
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries OPEC has a share of 81.89 % (1,214.21 billion barrels) of world crude oil reserves as against 18.11 % (268.56 billion barrels) of non – OPEC Members. The GCC countries has almost 40% share of world‟s crude oil reserves which make them strategically very important, especially for India.
1. CONCLUSION
Two Decade ago, India‟s Look East policy was an effort to cultivate extensive economic and strategic relations with the nations of Southeast Asia in order to bolster its standing as a regional power and a counterweight to the strategic influence of the People‟s Republic of China. It marked a strategic shift in India‟s perspective of the world. It was developed and enacted during the government of Prime Minister Shri. P.V.Narasimha Rao (1991–1996) and rigorously pursued by the successive administrations of Shri. Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1998–2004) and Dr. Manmohan Singh (2004–2014). Currently Prime Minister Shri.Narendra Modi is taking policy to next level as Act East Policy, with main objective is to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationship with countries in the Asia-Pacific Region. This Policy highlights the Importance of North-East of India and put it on priority.
India can contribute to GCC‟s socio-economic development through
. Global Health Care facility and Job Provider
. Provide Service in terms of IT&ITES, IoT, AI sectors and other Applications
. Travel and Tourism
. Exports of Machinery Equipments, Gems & Jewellary and Food Products
. Enhancing stability and Security in the high Seas of Gulf through participation in Anti- Piracy
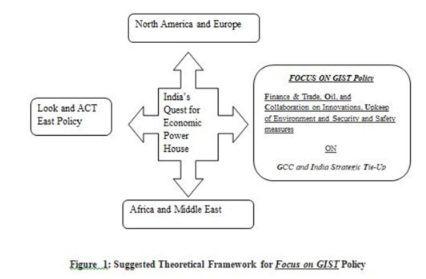
The Indian Economy is heading for a USD 5 Trillion with a growth rate of 7 %, she shall have a clear policy with GCC so to cooperate and collaborate with GCC in terms of Trade, Technology Transfer, Defence and Innovation. It is also important that India shall leverage its diaspora of 10 million NRI from the GCC to cement ties further. The Oil and Remittances could be the Key Quantitative elements while the Semiskilled/Unskilled workforce from India, Counter Terrorism, Cyber Security and Anti Piracy could act as Qualitative elements in bonding India‟s ties further with GCC. In this paper we suggest FOCUS on GIST policy. GIST Means GCC and India Strategic Tie-Up. Focus will signify Finance & Trade, Oil, and Collaboration on Innovations, Upkeep of Environment and Security and Safety measures. Better management of Crude oil from GCC in terms of supply and pricing along with the increased flow of remittances to India from GCC region could have a great impact on Indian trade balance and overall economic development. The Focus on GIST policy will also help in augmenting India‟s integration with Middle East Region. Look and Act east policy if embedded with FOCUS on GIST policy, will stimulate a great thrust for India‟s Quest for Economic Power House.
NOTES:
1 see http://www.worldstopexports.com/crude-oil-imports-by-country/date accessed February, 20th, 2019.
2 see https://www.nriol.com/indiandiaspora/statistics-indians-abroad.asp date accessed February 20th, 2019.
3 see https://www.chemarc.com/content/article/polymer-potpourri–indias-lack-of-credible-fuel- policy-a-matter-of-high-concern/5a9fbefda64f4346a9d2e4e6 date accessed February 20th, 2019.
4 see https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/china-gulf-economic-relations date accessed February 24th, 2019
REFERENCES:
Abdelal R., Khan Ayesha and KhannaTarun (2008), “Where Oil Rich Nations are Placing Their Bets”, Harvard Business Review,September, pp. 119-128
Alam Imran and Ahmed Shahid (2018), “A Panel Gravity Model Analysis of India‟s Export to Gulf Cooperation Council Countries”, Journal of International Economics, Vol. 9, No.2, January –June ,pp. 72-86
Habibi Nader (2011), “Growth in economics relations of China and India with GCC Countries”, Asian-Pacific Economic Literature, Vol. 25,Issue 2, pp. 52-67
Xuming QIAN & Jonathan FULTON(2017), “China-Gulf Economic Relationship under the “Belt and Road” Initiative”, Asian Journal of Middle Eastern and Islamic Studies, 11:3, 12-21, DOI: 10.1080/25765949.2017.12023306 date accessed February 24th, 2019 Authors:
Dr Nitin S. Kulkarni- Associate Professor, MET‟s Institute of Management, Bandra (w) Mumbai Pranali Bandekar – 2nd Year Student Perusing Masters in Management Studies at MET‟s Institute of Management, Bandra (w) Mumbai

